Search results
Query: wire length
Links: 67 | Categories: 0
-
How to Design and Build a Field Expedient End-Fed Half-Wave Antenna for 20m, 40m and 80m. This Shorty 80m EFHW comprises a 49:1 autotransformer (to match the very high impedance at the end of a half-wave wire), a half-wavelength wire for 40m (also a quarter-wavelength for 80m), a loading coil and a short tail wire. The coil and the short tail wire (about 6 feet) make up the other quarter wave on 80m.
-
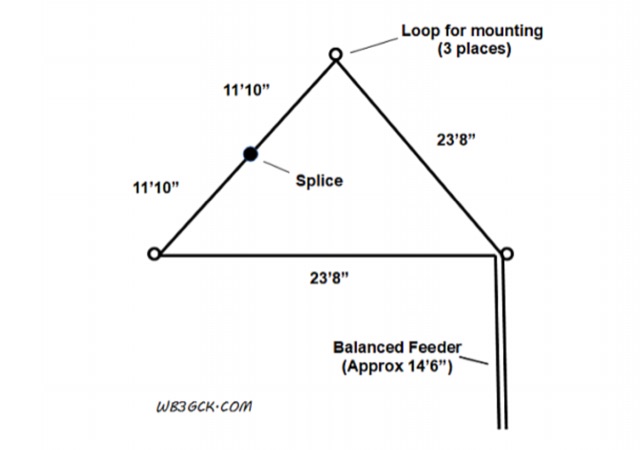
The antenna I built was inspired by a portable delta loop designed by Doug DeMaw, W1FB. Given that I constrained myself to a 50-foot roll of speak wire, I scaled my antenna for the 20M band. Using the formula, 1005 divided by the frequency in megahertz, I calculated a total length of 71 feet (21.6 meters) for the center of the 20M band.
-
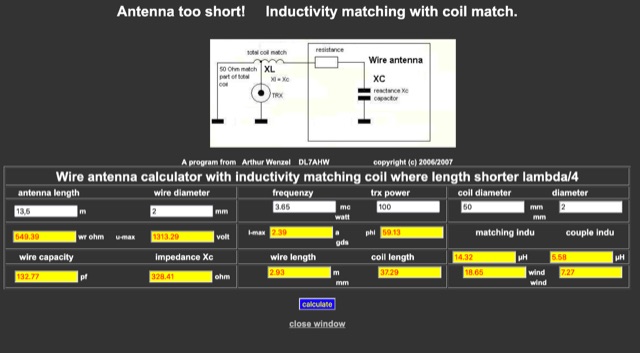
Wire antenna calculator with inductivity matching coil where length shorter lambda/4
-
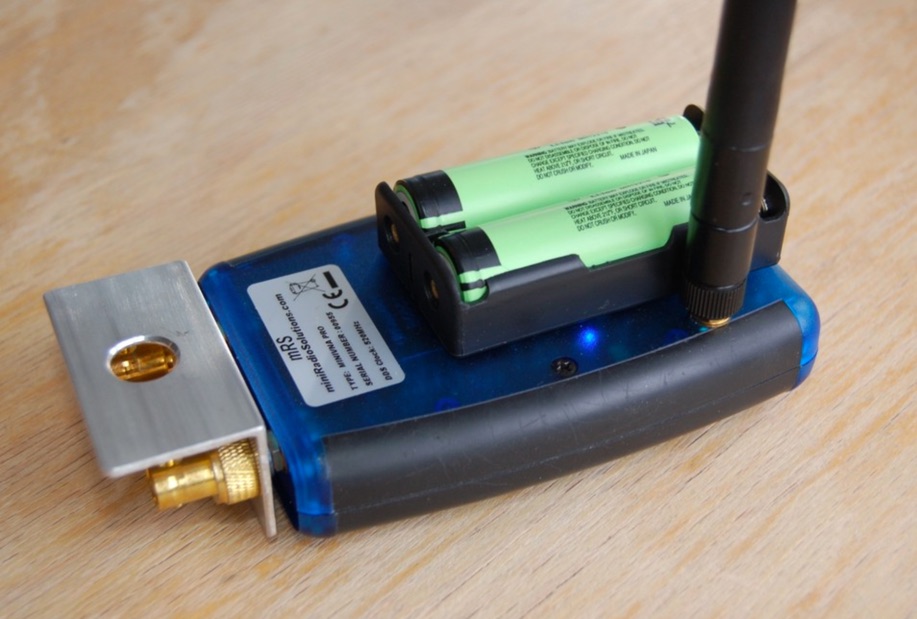
The mini Radio Solutions miniVNA PRO is the only affordable vector network analyser (VNA) I know of that offers remote wireless operation. This is very interesting because it allows to measure the input impedance of HF antennas installed at height without having to deal with coax cable lengths, baluns nor common mode suppression chokes. However, to render the miniVNA PRO truly field proof, it requires a number of significant modifications.
-
A Home made antenna tuner for QRP transceivers. This small tuner is the ideal for portable operations with random length wires or whenever you have not a resonant antenna.
-
The article offers practical guidance for setting up Field Day antennas, emphasizing the unpredictability and need for quick adaptations. It provides a comprehensive table of wire lengths for various bands and antenna types, using 1mm bare wire, in both metric and Imperial units. The author highlights the benefits of this table in saving time and reducing errors. While acknowledging potential variations due to construction and environmental factors, the article presents the table as a reliable starting point, with plans for future updates to include more bands and antenna types. This resource is valuable for ensuring efficient and accurate antenna setup during Field Day events.
-
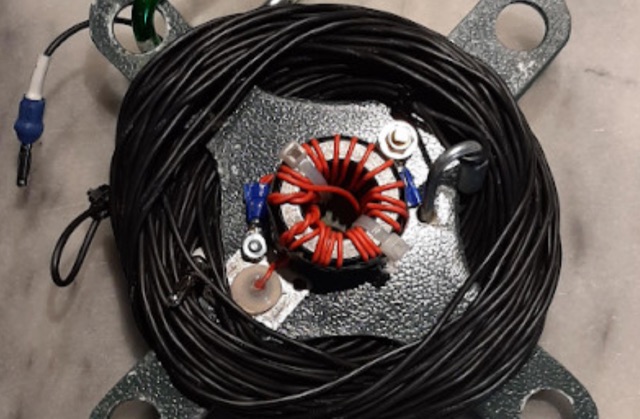
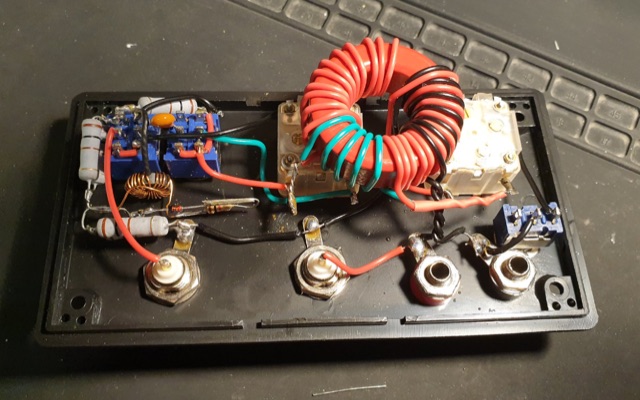
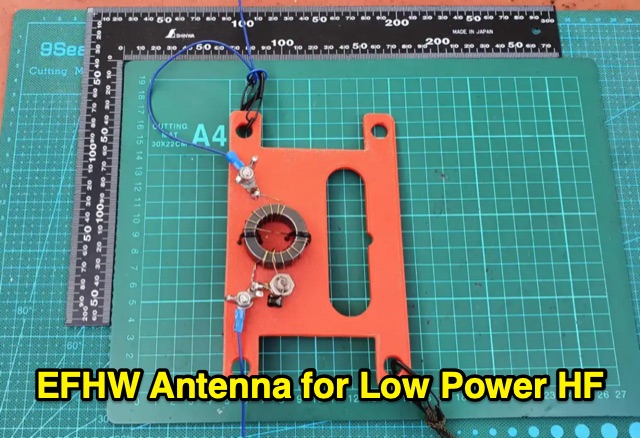
This describes a homebrew End-Fed Half-Wave (EFHW) antenna for low power SOTA, Parks and Field Day events. Made with readily available materials, it offers a resonant antenna in 40/20/15/10m bands without requiring an antenna tuner. The 19.8m long radiator wire in an inverted V configuration achieves VSWR below 1.5:1 for voice. CW users might need to adjust the length. Details include materials list, fabrication of the end insulator, and the 49:1 impedance transformer construction with a circuit diagram.
-
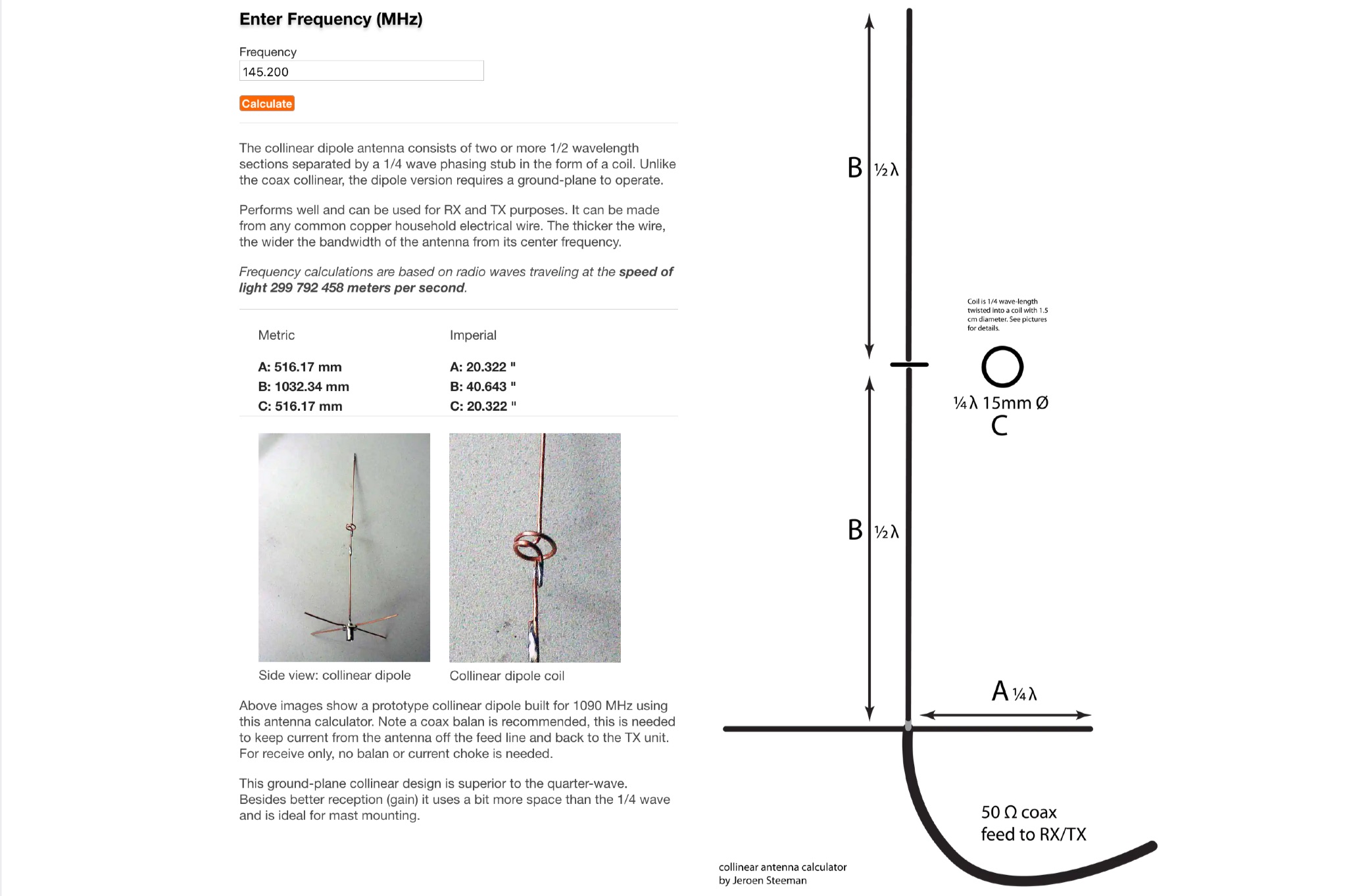
This page offers an online antenna designer to calculate the dimensions for a collinear dipole antenna at a specified frequency. The collinear dipole antenna is constructed with multiple 1/2 wavelength sections separated by a 1/4 wave phasing stub in the form of a coil. It requires a ground-plane to operate and can be used for both receiving and transmitting purposes. The antenna can be made from common copper wire, with thicker wire providing a wider bandwidth. The calculations are based on radio waves traveling at the speed of light. Ideal for ham radio operators looking to build their own antenna for improved reception and transmission.
-
This page discusses the CLEFHW (Coil Loaded End-Fed Half-Wave) antenna, a portable variation of the popular EFHW design for ham radio operators. The article explains how the CLEFHW allows for backpack portable operation without the need for trees or poles, making it ideal for POTA activations and rapid deployment scenarios. The author details the design, optimization for 20m band, and compares efficiency to full-length wire antennas. Suitable for hams interested in portable antenna solutions and quick setup options for amateur radio activities.
-
WB5NHL describes setting up a 160-meter antenna on a small suburban lot, where standard options like Beverage antennas and 1/4 wavelength verticals require extensive space and ground systems. Instead, Guy Olinger's Folded Counterpoise (FCP) provides a solution. The FCP minimizes ground losses by using a folded wire design, allowing effective antenna placement in limited space. The FCP, fed with an isolation transformer, enabled WB5NHL's first 160-meter antenna installation, offering improved performance despite space constraints.
-
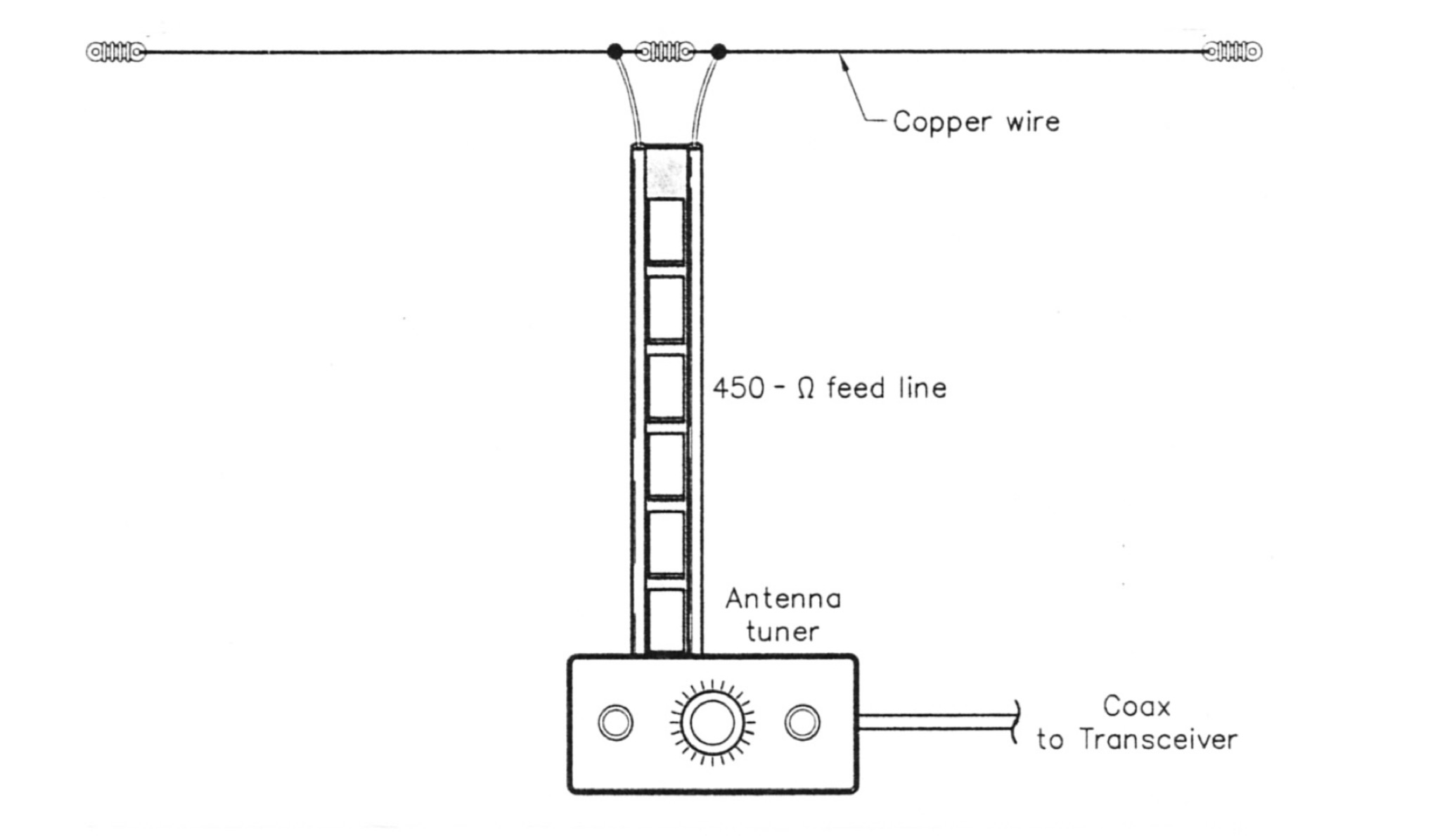
The multiband tuned doublet, or center-fed Zepp, is a simple and efficient HF antenna that operates effectively across most amateur bands using a balanced parallel-wire feedline and antenna tuner. Unlike coax-fed dipoles, it tolerates impedance mismatches with minimal loss. By selecting suitable feedline and dipole lengths, one can achieve stable multi-band operation. While it doesn’t match monoband Yagis, it offers excellent performance, low cost, and broad coverage. Its radiation pattern and efficiency vary with frequency, but it remains a practical and versatile solution for HF operators.
-
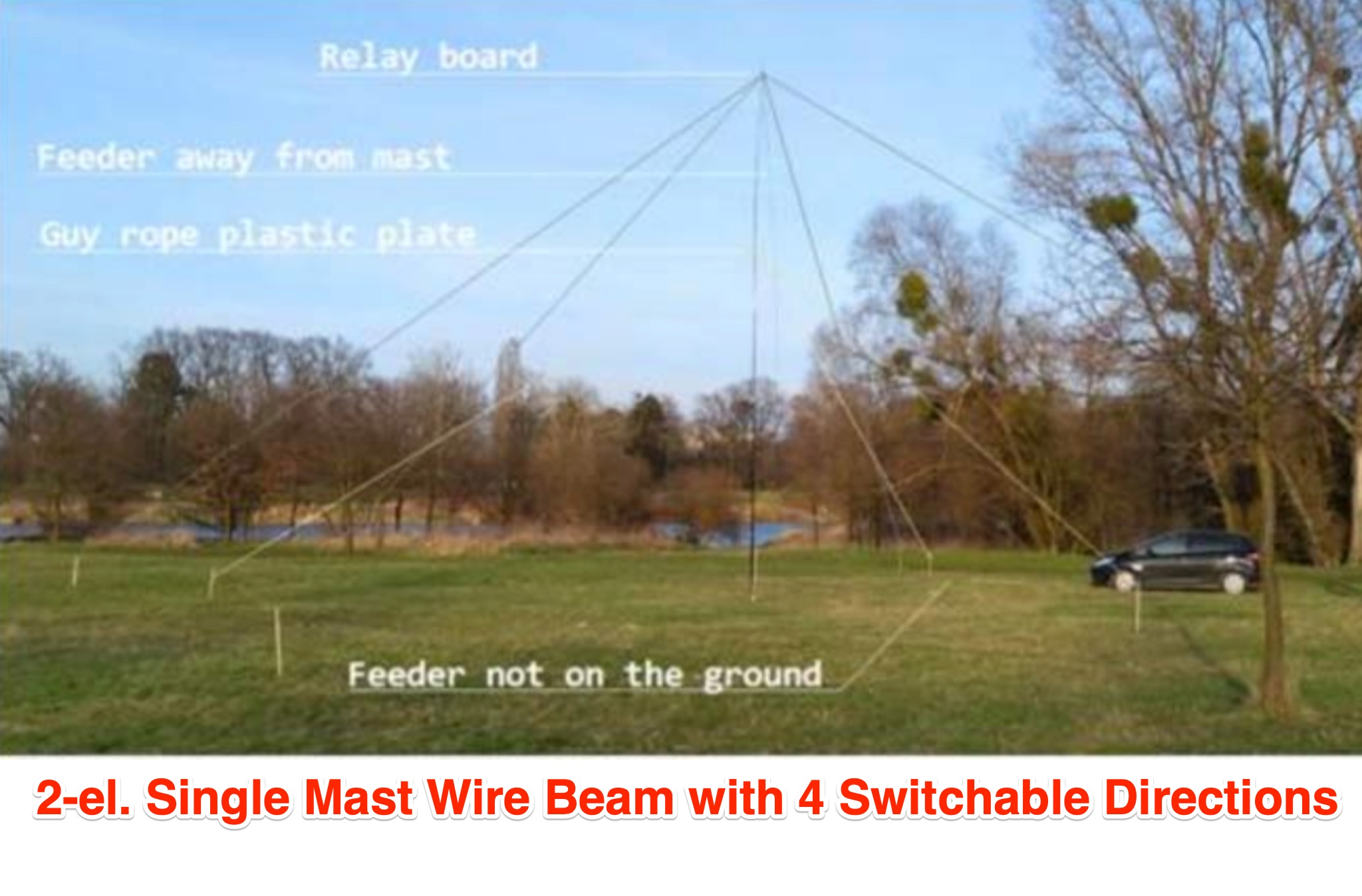
This article discusses the design and implementation of a 2-element wire beam antenna for the 20 meter band, suitable for field day operations with 4 Switchable Directions. The antenna is configured with sloped wires in an inverted V shape, with a specific design to achieve directional properties. The author tested the antenna design using MMANA and NEC2 software, based on a solution published in QST. Detailed diagrams and instructions are provided for constructing the antenna on top of a 12 meter mast, with specific wire lengths and positioning to ensure optimal performance. This resource is valuable for hams looking to build a directional antenna for the 20m band and improve their field day setup.
-
This article explores Beverage antennas, a type used for low-frequency radio reception. Despite the mystique, they are relatively simple wire antennas placed near the ground. Their key benefit is improved signal-to-noise ratio by rejecting unwanted signals. While lengthier antennas offer better reception, even shorter versions (around 200 feet) can improve DX reception compared to traditional antennas.
-
Learn how to build a simple transmitter called the 'Easy Ten' that can be easily heard at a distance of 10 miles using a random length wire antenna thrown into a tree. This article focuses on working with frequencies in the 3.5 and 7 MHz range without the need for complex setups like coax lines or baluns. The author shares their experience of making contacts across the Pacific Ocean and the United States using just one watt of output power and simple antennas. Discover how to optimize signal output using a homemade level meter made from a DC microameter and a germanium diode.
-
This project outlines a simple, cost-effective 40m band HF dipole antenna design, ideal for beginners. Constructed with insulated copper wire and a 1:1 balun, it offers a 50-ohm impedance, suitable for both 40m and 15m bands due to the harmonic relationship. Calculations account for a K factor, ensuring optimal length and performance. Antenna modeling with 4NEC2 confirms practical access to both bands, though real-world results may vary. Lightweight materials and straightforward assembly make it an accessible and versatile amateur radio solution.
-
The 40-meter delta loop beam by K4TX/K4GE is an efficient wire antenna with two key features: 3/8 wavelength feedline sections used to tune a non-driven loop as a reflector, and an upside-down delta configuration for greater height. This enhances front-to-side rejection and provides 10-15dB front-to-back performance, making weak DX signals easier to hear on noisy bands. For 7.0 MHz, feedline lengths vary by coax type. The antenna works well, but regular coax switches may not be suitable, and a custom switch box may be needed
-
This paper presents an 80 meter wire 3-element beam antenna in an inverted-V configuration, designed for limited-height towers. Using EZNEC modeling, the antenna features a central parasitic reflector and two switchable driven elements at each end, enabling NE/SW coverage without moving parts or networks. Element lengths are optimized for SSB (3.8 MHz) and CW (3.5 MHz) operation, with a 50 Ω feed and rope-supported boom. The design delivers high gain, effective takeoff angles, and excellent reception, confirmed in real-world DX contest operation. Its simplicity, reliability, and ease of construction make it ideal for operators seeking performance without complex matching systems.