Search results
Query: yagi antennas
Links: 150 | Categories: 7
-
Profesional GPS, GSM, Telematics, Yagi, WIFI antennas by 2J antennas
-
A great and efficient monoband VHF portable antenna. The article consist of two version of a 12.5 Ohm 3 elements yagi beam antenna plans for the two meter band, a full sized and a shortened version expecially designed for the SSB and CW on 144 MHz.
-
Article on Yagi and Log periodic antennas by Tom, K1JJ
-
A view of the NCDXF Multiband beacon and a cluster of stacked yagi antennas.
-
Basic priciples of Yagi antennas and its variations like Quagi antennas, Quad antennas includes pictures, drawings and online calculators by KN9B
-
Dubus article about DL6WU long yagi antennas for 23 cm band Article is both in german and english. Yagi antennas are valid alternative to dishes for troposcatter operations. This article explains design and mechanical data for 1296 MHz Yagi Antennas
-
-
A practical guide on hombrewing Yagi antennas, including notes on Driven Element, Transformation & Symmetrising Coax Lines, Full Boom length vs. electrical length, Elements & Insulators on Boom and additional tips and tricks, in English and German
-
Article on 50 Mhz Yagi Antennas stacking by OH1ZAA/NN0Y
-
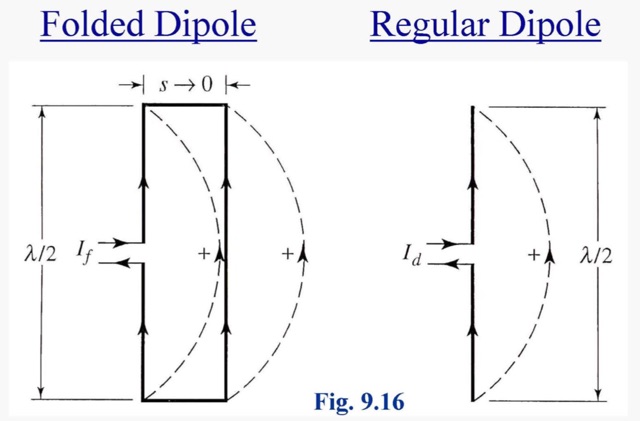
A folded dipole is an antenna, with two conductors connected on both sides, and folded to form a cylindrical closed shape, to which feed is given at the center.
-
An article describing basic concepts of antenna radiation, and in particular directional antennas like Yagi antennas or Quad antennas and how they determine the direction or signals.
-
-
A page with an embedded video about a two elements yagi antenna for 28 MHz based on the original antenna design by VE7CA
-
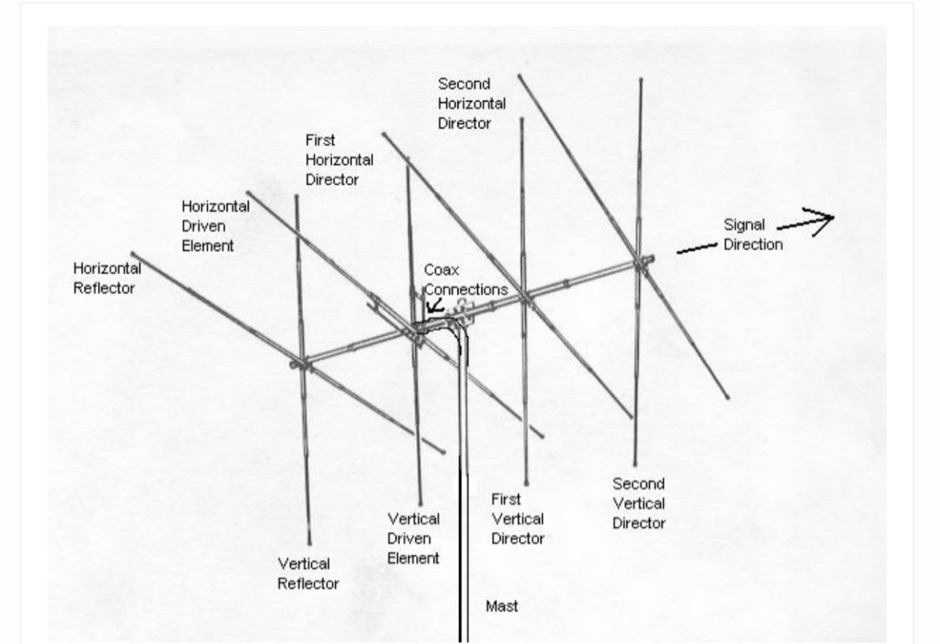
The video delves into the fascinating science behind antennas, which are crucial for receiving and transmitting electromagnetic waves. It explains how antennas convert electric signals into electromagnetic waves for transmission, and how they operate through the oscillation of positive and negative charges in dipole arrangements. Practical antenna implementations, such as dipole antennas for TV reception and Yagi-Uda antennas with reflectors and directors, are also discussed alongside modern dish TV antennas with parabolic reflectors for signal processing. It's a comprehensive overview of how antennas work and their significance in communication technology.
-
Stacking yagi antennas for 50 Mhz band article by by Zaba, OH1ZAA/NN0Y
-
On-line shop for coax cables, RF connectors, Lightning protectors, Create antenna rotators, antenna masts and mounts, amateur antennas by FlexaYagi, Tonna F9FT, ANjo-Antennen and M2 Antennas based in Eggolsheim Germany
-
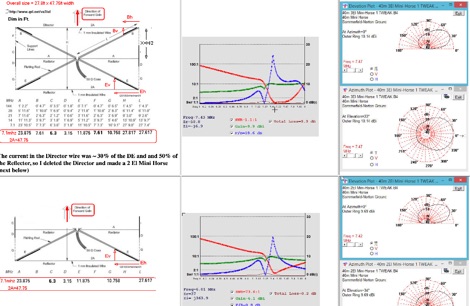
This page describes a comparison study on seven different beam antennas for 40 meters band. Yagi antennas, moxon antennas, mini horse all antennas are described with schema diagram , azimuth plot and SWR F/B Gain diagram
-
This is a synopsis of a talk presented to the Sydney VHF DX GROUP by VK2ZAB on how, when and why is convenient to build a Yagi antenna stack.
-
Antennas for the 1296 MHz based on the construction plans of some Yagis 35 elements by DL6WU, F9FT, DJ9YW. These antennas features a boom of about 3 m and gives a gain of about 17.8 dBd
-
A short 3 element LFA Yagi for 50MHz with a 1.94M boom. This antenna has been designed in order to minimise the upward and downward lobes typically seen the the EL plane on Yagi antennas.
-
A collection of 450 MHz Cheap Yagis that have proven great portable operations, back-packing and transmitter hunts, and are something inexpensive you can throw up in the attic for that weak repeater
-
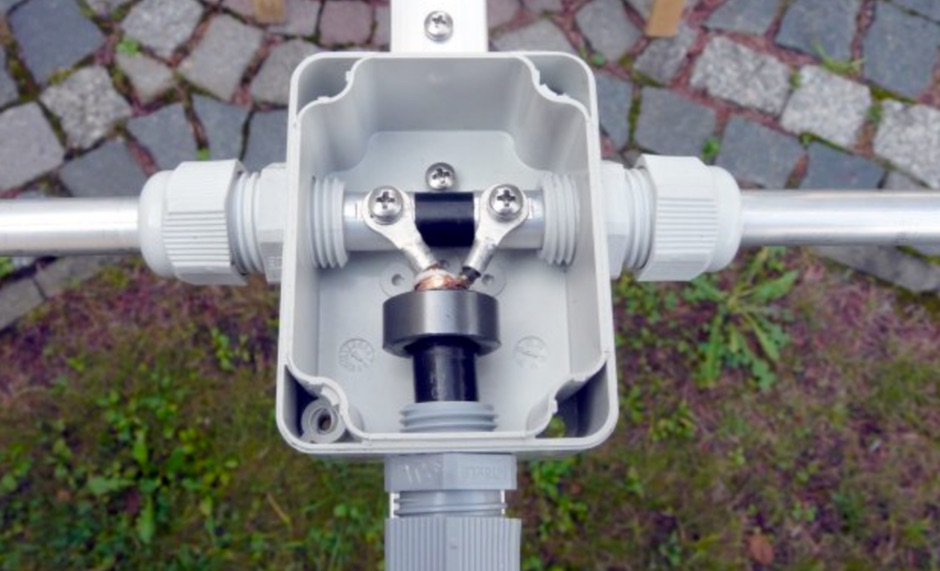
German antenna parts dealer, provides antenna element holders, element clamps for yagi antennas, junction boxes, aluminium plates and rods. Offers also Rope tensioners, plugs and adapters and any additional part you need when you want to make your own antenna.
-
10 Elements Cross-Yagi Antenna for 433 MHz. The base of the 10el antenna is the recalculated RA6FOO antenna.Circular polarization is realized - by a phasing quarter-wave line, matching of horizontal and vertical polarization antennas
-
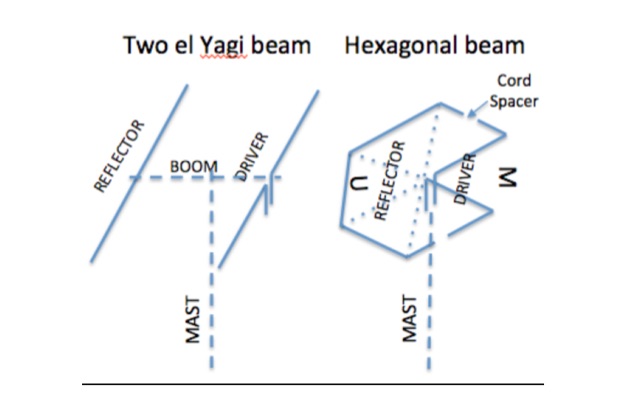
A hexagonal beam is a form of the Yagi antenna which is based on parasitic principles developed early in the last century in Japan for achieving gain in one direction.How HexBeam antennas works. A hexagonal beam operates exactly like Yagi antenna, but instead of a driven element that is straight like a dipole, it is a wire bent into the shape of the letter M.
-
The calculator designs the Yagi-Uda antenna based on the DL6WU model with boom correction, following the G3SEK-DL6WU method. It optimizes the antenna for maximum gain and allows adjustment of passive elements without affecting SWR. DL6WU antennas are known for their high gain, minimal sensitivity to nearby objects, and stable performance in various weather conditions.
-
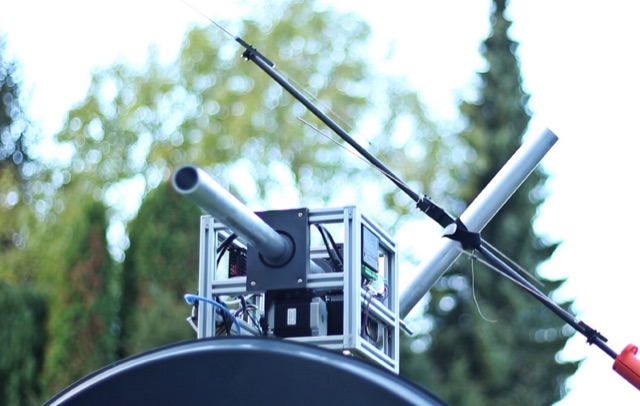
Tysonpower details a DIY AZ/EL antenna rotator project designed for under €150, inspired by the Satnogs Tracker. Constructed with 2020 aluminum extrusion and NEMA23 stepper motors, the rotator is controlled via an Arduino Nano. It effectively tracks smaller antennas like Yagi, though struggles with heavier dishes. STL files are available on Thingiverse.
-
A lightweight PVC hand-held telescopic 2 element 2m (145 MHz) yagi using two pairs of TV rabbit ear antennas as the driven and reflector elements. Approximate directional gain is 5dB.
-
144MHz 2m Portable Yagi VHF Beam Antenna. This page contains construction details on a 2 metre 144MHz VHF Yagi beam antenna, designed for portable use.
-
The original HEXBEAM was developed by Mike Traffic, N1HXA, in the early nineties. It is true that an M over W configured yagi antenna that resembled a butterfly was earlier tried successfully. But the advanced electrical design, the characteristic nesting concept and central terminal post that enable the multi band functionality along with the basic hardware design were all developed by Mike Traffie.
-
In this article the author describes his personal experience on some antennas for 50 MHz he tested on the field, the six meter Dipole, Vertical, Moxon, a 3 element Yagi and an Omniangle antenna.
-
Learn about the practical design and construction of Yagi antennas for ham radio operators. This post explores the benefits of Yagi antennas in receiving and transmitting RF signals, concentrating signal energy in one direction for long-distance communication. Discover the theory behind Yagi antennae, the importance of element size and spacing, and the resources available for sizing and construction. Whether you're interested in OTA television or amateur radio communication, understanding Yagi antenna design can enhance your signal reception and transmission capabilities.
-
This article discusses the Disk-Yagi antenna, also known as the "gun antenna," popularized by the video blogger KREOSAN. It explains the design, differences from standard Yagi-Uda antennas, and key features like the use of patch antennas and the integration of MIMO technology. The article covers the construction, tuning challenges, scaling issues, and provides insights on practical applications, such as optimizing signal performance with a 75-ohm antenna. It emphasizes that while DIY versions may vary, careful tuning and design are crucial for effectiveness.
-
This Satellite Antenna Elevation System project involves mounting horizontally polarized Yagi antennas on a fiberglass reinforced polymer (FRP) crossboom. A Yaesu G-800DXA azimuth rotator is in place, requiring only an elevation rotation system. Elevation is controlled by a 12VDC linear actuator connected to a U-bolted arm on the crossboom, rotating within a DIY bearing arrangement. Common handyman tools suffice for assembly. The setup includes FRP crossboom, aluminum tubing, PVC couplers, nylon camshaft bushes, and a K3NG-based controller for azimuth and elevation control. Detailed guides and resources are available online.
-
Method, Units of Measure, and the Dipole Standard of Reference. This article helps in understanding where does beam gain come from in directional aerials like in example Yagi antennas.
-
This DIY guide details constructing a 5-element Yagi antenna for VHF frequencies. Yagi antennas offer directional signal transmission/reception compared to omnidirectional ones. The guide covers material selection (aluminum, screws, etc.), design using software or formulas, and step-by-step assembly including cutting elements, drilling holes, and attaching the coaxial cable. While calculations are provided for a 146 MHz design, adjustments are necessary for different frequencies. Safety precautions and potential result variations are emphasized.
-
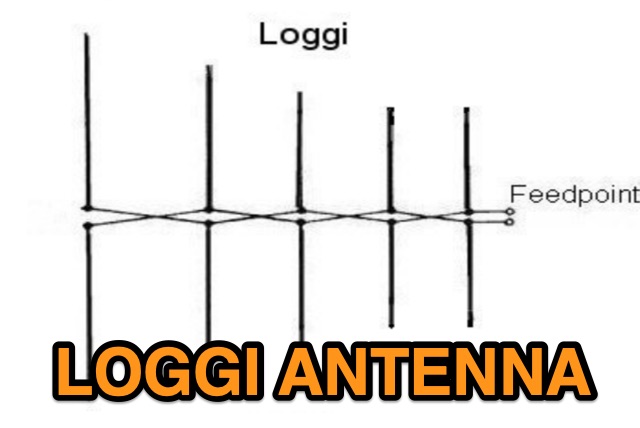
This project introduces the Loggi, a hybrid antenna merging the wide frequency coverage of log-periodic dipole arrays (LPDA) with the high gain and front-to-back ratio (F/B) of Yagi antennas. Traditional LPDAs span broad frequencies with moderate gain and low VSWR, while Yagis provide high gain and F/B over narrow bands. By analyzing high-Tau LPDA designs, it was found they could nearly match the gain of VHF/UHF Yagis while maintaining excellent patterns, F/B, and front-to-rear ratios (F/R). Optimizing specific elements for target frequencies (e.g., 144.1 MHz) led to the Loggi, which uniquely features all driven elements without passive directors or reflectors. This design effectively functions as a narrowband optimized LPDA, with front elements acting like Yagi directors and rear elements like Yagi reflectors, thus enhancing gain and directional characteristics while retaining broad frequency versatility.
-
This presentation on antennas is a practical guide for amateur radio operators. The key takeaway is that the best antenna for your station depends on your constraints and goals. There is no magic solution and buying a wire antenna is not recommended as it might be expensive and not as effective. The presentation covers different antenna types including dipoles, verticals, Yagis and loop antennas. Important factors to consider when choosing an antenna include SWR, feeder types, and whether you need a balun. The author emphasizes that ATUs don’t improve a poor antenna and advises against obsessing over SWR readings.
-
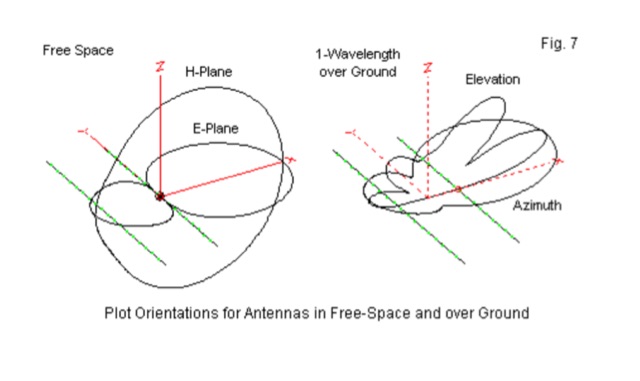
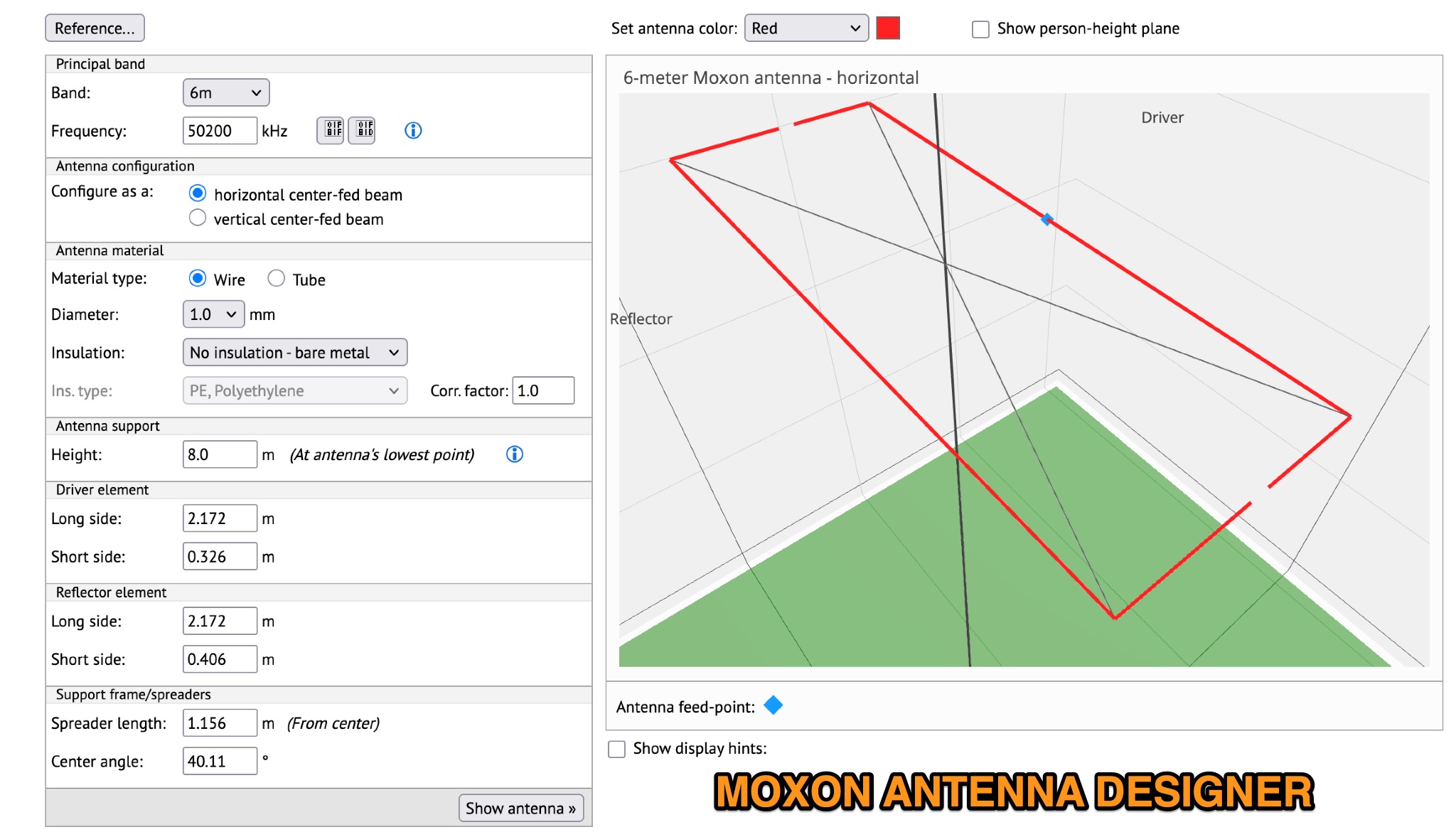
This page provides information on designing a lightweight Moxon antenna for the upper HF bands and VHF. The Moxon antenna is a compact version of a 2-element Yagi with folded elements, offering good forward gain and a high front-to-back ratio. It is designed for a single band with a feed-point impedance close to 50 ohms. Hams can orient the antenna horizontally or vertically, with polarization following the configuration, affecting radiation patterns. The page allows users to generate radiation pattern plots, VSWR charts, antenna currents diagrams, and Smith charts for their antennas on different ground types, helping them understand antenna performance in the field.
-
This document provides a detailed guide on constructing and mounting a folded dipol for the 146 MHz frequency in a vertical configuration to be used in Yagi antennas. The step-by-step instructions and diagrams included make it easy for hams to build and set up this type of antenna. Understanding and implementing this design can enhance the performance of radio communication for Amateurs operating in the 2-meter band. Whether you are looking to improve your signal strength or experiment with antenna designs, this resource offers valuable insights and practical information.
-
This page provides construction details for a 4-element 10-meter Yagi antenna with 28 Ohm impedance. It includes information on the elements, positions, diagrams, and data related to frequency, gain, front-to-rear ratio, radiation resistance, SWR, and loss. The content is aimed at hams or radio operators interested in building and optimizing Yagi antennas for the 10-meter band.
-
G6HKS Yagi Kits & Parts provides material kits for building high-performance PowAbeam Antennas, ideal for VHF/UHF enthusiasts interested in DXing. The kits feature advanced Yagi designs, including the unique ParAclip system, ensuring exceptional all-weather stability and minimizing detuning effects. With resources, tips, and support, the site aims to make antenna construction straightforward for amateur radio operators. The focus is on delivering top-tier performance at competitive prices, empowering users to build and enjoy their own high-quality antennas.
-
Rob Conklin N4WGY delivered an informative presentation on Hexagonal Beam antennas (Hex Beams), detailing their construction, performance, and benefits over traditional multiband Yagi antennas. He highlighted their cost-effectiveness, lower wind loading, lightweight design, and multi-band capabilities without requiring traps. Conklin also discussed the improved G3TXQ design, which offers better SWR performance across ham bands. The presentation included practical construction tips, resource recommendations, and demonstrations of performance analysis tools, making it a valuable resource for both novice and experienced antenna builders.
-
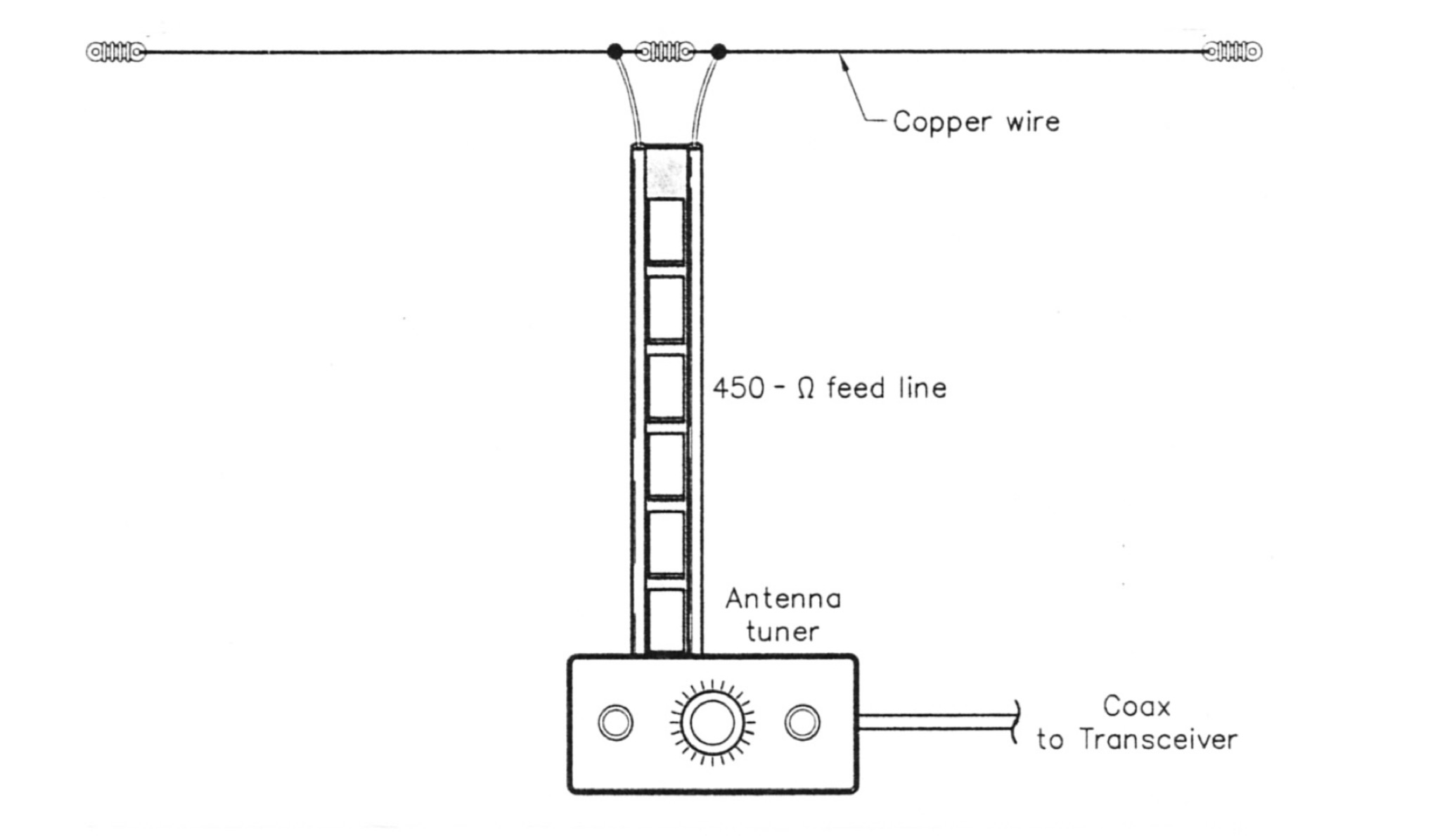
The multiband tuned doublet, or center-fed Zepp, is a simple and efficient HF antenna that operates effectively across most amateur bands using a balanced parallel-wire feedline and antenna tuner. Unlike coax-fed dipoles, it tolerates impedance mismatches with minimal loss. By selecting suitable feedline and dipole lengths, one can achieve stable multi-band operation. While it doesn’t match monoband Yagis, it offers excellent performance, low cost, and broad coverage. Its radiation pattern and efficiency vary with frequency, but it remains a practical and versatile solution for HF operators.
-
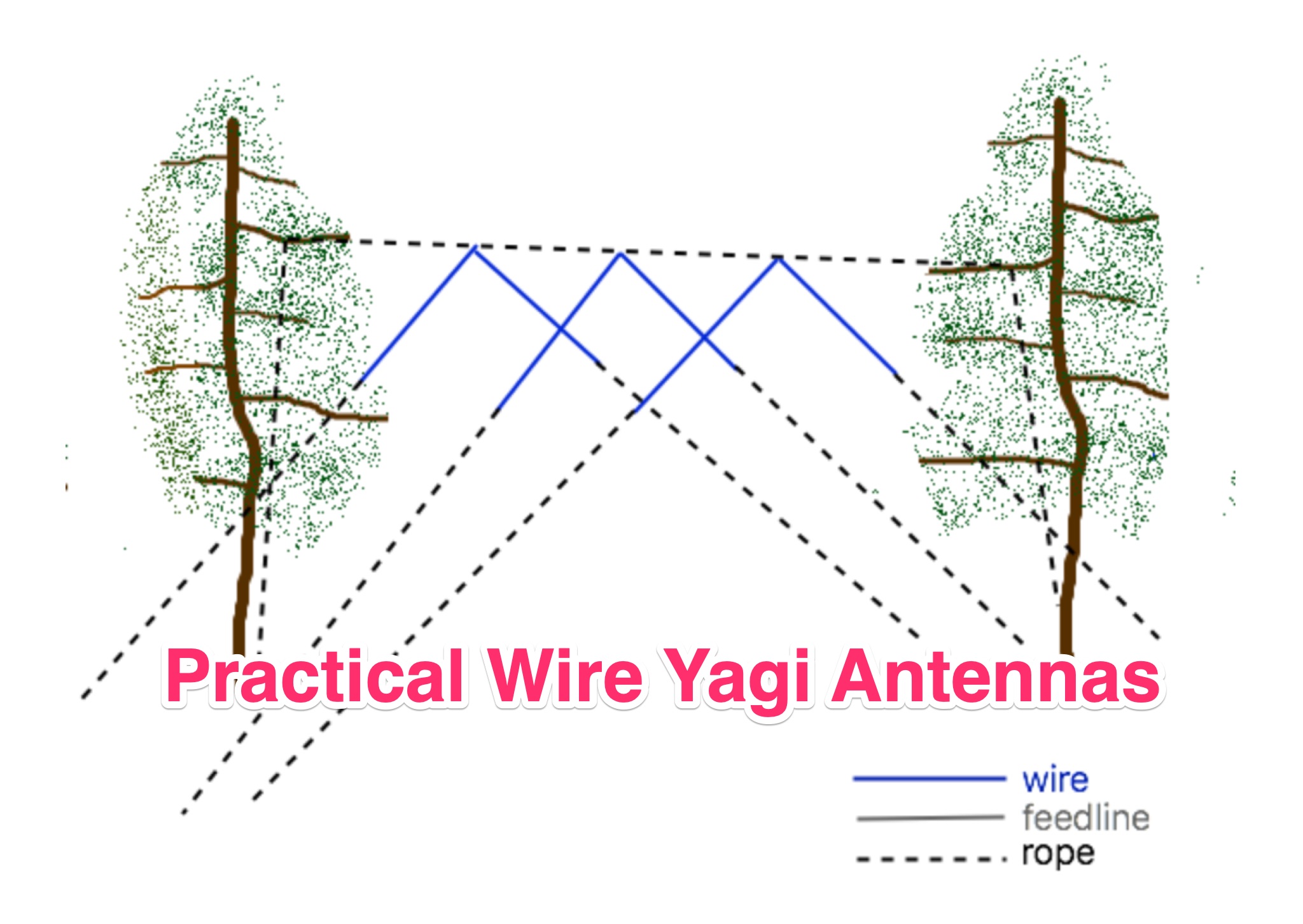
Learn how to build wire Yagi antennas for your ham radio setup. Discover how smaller wire elements can offer practical and portable options for temporary operations. Explore designs like the Hex Beam, Spider Beam, and Moxon that require less mechanical complexity and can be easily rotated or supported. Find out how to construct and hang wire Yagis from ropes, trees, or masts with inverted vees or horizontal elements. Get tips on element positioning, gain, and beamwidth considerations. Follow simple construction steps using a rope boom and marking element positions for efficient assembly. Enhance your ham radio experience with versatile wire Yagi antennas.
-
In this article, VE3VN shares their experience constructing a vertical polarized 30 meter delta loop antenna. They discuss the challenges and solutions encountered during the design and deployment process, offering valuable insights for ham radio operators looking to build their own antennas. The author explains the benefits of using a vertically polarized delta loop, its simplicity, omni-directional coverage, and lack of interference with horizontal yagis. This detailed account provides a practical guide for hams facing similar mechanical and electrical issues in antenna construction.
-
This article from the July 1976 issue of Radio REF discusses the trend of large antennas for ham radio operators on the low bands. It specifically focuses on a Yagi 2 element antenna for the 80m band, detailing its construction and functionality. The author explains how the antenna can be switched between directing signals towards the West or East using a switch at the station. The article also provides technical details on the lengths of the director and reflector elements, and how they impact the antenna's performance. A useful resource for hams looking to build or understand Yagi antennas for the 80m band.
-
This page provides a detailed review and installation experience of a new 6 and 2 meter dual band Yagi antenna. The author shares insights on the purchase process, shipping, assembly, and performance of the antenna in their backyard setup. The content is useful for hams looking for information on dual band Yagi antennas, especially those interested in improving their contest operations or backyard installations. The author's personal experience and challenges with mounting the antenna on a small push-up mast are also discussed.
-
YAGio 1.01 is a Windows-based software for designing DL6WU long Yagi antennas on VHF and UHF frequencies. It supports Windows 2000, XP, Vista, 7, and likely 8. Using keyboard commands, users input specifications such as frequency, gain, and element diameters, and YAGio generates the design. You can download latest Yagio version from this page. Results can be saved in YIO, NEC, YAG, MMA, and YC6 formats, or printed directly.
-
This paper by Leif Asbrink (SM 5 BSZ) presents a practical approach to designing very high gain Yagi antennas, focusing on the "brute force" optimization method. The method, described in a previous article, ensures convergence independent of initial guesses. The paper provides detailed tables of element lengths and positions for Yagi antennas optimized for 144.1 MHz with a 50-ohm feed point impedance, aiming for minimal losses and high accuracy in comparisons.
-
SAT filters ensure effective full-duplex satellite QSOs by mitigating interference between 145 MHz uplink and 435 MHz downlink signals. Custom coaxial and SMD-based filters address transmitter harmonic interference and improve receiver isolation, achieving over 70 dB suppression in the undesired band. Designed for simplicity, these filters maintain optimal VSWR and are housed in shielded brass enclosures. Practical implementations with Yagi antennas demonstrate compatibility with SDR systems, enabling seamless communication even in challenging satellite conditions, such as low-elevation passes and DX pile-ups.